Constant,variables,keywords in c language
Constant in c programming language:-
Any information is constant.
data=information=constant
Types of constant:-
There are two types of constant,which are given below such as.
1. Primary Constant:-
i. Integer constant.
ii. Real constant
iii. Character constant.
2. Secondary constant:-
i. Array
ii. String constant
iii. Pointer.
iv. Union.
v. Structure.
vi. Enumerator.
1. Integer constant:-
Any information is constant.
data=information=constant
Types of constant:-
There are two types of constant,which are given below such as.
1. Primary Constant:-
i. Integer constant.
ii. Real constant
iii. Character constant.
2. Secondary constant:-
i. Array
ii. String constant
iii. Pointer.
iv. Union.
v. Structure.
vi. Enumerator.
1. Integer constant:-
. An integer constant must have at least one digit.
. It must not have a decimal point.
. It can either be positive or negative.
- No commas or blanks are allowed within an integer constant.
- If no sign precedes an integer constant, it is assumed to be positive.
- The allowable range for integer constants is -32768 to 32767.
4. real contant :-
- A real constant must have at least one digit
- It must have a decimal point
- It could be either positive or negative
- If no sign precedes an integer constant, it is assumed to be positive.
- No commas or blanks are allowed within a real constant.
3. Character AND STRING CONSTANTS IN C:-
- A character constant is a single alphabet, a single digit or a single special symbol enclosed within single quotes.
- The maximum length of a character constant is 1 character.
- String constants are enclosed within double quotes.
How to use of Constant in C language:-
#include <stdio.h>
#define height 100
#define number 3.14
#define letter 'A'
#define letter_sequence "ABC"
#define backslash_char '\?'
void main()
{
printf("value of height : %d \n", height );
printf("value of number : %f \n", number );
printf("value of letter : %c \n", letter );
printf("value of letter_sequence : %s \n",letter_sequence);
printf("value of backslash_char : %c \n",backslash_char);
}
Output of the above program:-
value of height : 100
value of number : 3.140000
value of letter : A
value of letter_sequence : ABC
value of backslash_char : ?
value of number : 3.140000
value of letter : A
value of letter_sequence : ABC
value of backslash_char : ?
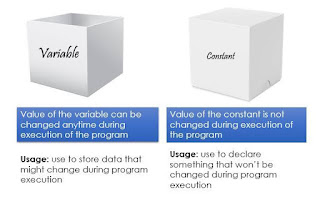
Variables in C language:-
A variable in simple terms is a storage place which has some memory allocated to it. Basically, a variable used to store some form of data. Different types of variables require different amounts of memory, and have some specific set of operations which can be applied on them.
Variable declaration:-
typical variable declaration in such a form-
type variable_name;
Declaration for multiple variables:-
type variable_name1, type variable_name2, type variable_name3..................type variable_namen;
A variable name can consist of alphabets (both upper and lower case), numbers and the underscore ‘_’ character. However, the name must not start with a number.
Output-
a
Keywords are specific reserved words in C each of which has a specific feature associated with it. Almost all of the words which help us use the functionality of the C language are included in the list of keywords. So you can imagine that the list of keywords is not going to be a small one!
There are a total of 32 keywords in C:
auto break case char const continue
default do double else enum extern
float for goto if int long
register return short signed sizeof static
struct switch typedef union unsigned void
volatile while
Most of these keywords have already been discussed in the various sub-sections of the C language, like Data Types, Storage Classes, Control Statements, Functions etc.
Let us discuss some of the other keywords which allow us to use the basic functionality of C:
auto:-
The auto keyword declares automatic variables. For example:
auto int var1;
This statement suggests that var1 is a variable of storage class auto and type int.Variables declared within function bodies are automatic by default. They are recreated each time a function is executed.
Since, automatic variables are local to a function, they are also called local variables. To learn more visit C storage class.
break and continue:-
The break statement makes program jump out of the innermost enclosing loop (while, do, for or switch statements) explicitly.
The continue statement skips the certain statements inside the loop.
for (i=1;i<=10;++i)
{
if (i==3)
continue;
if (i==7)
break;
printf("%d ",i);
}
switch, case and default:-
The switch and case statement is used when a block of statements has to be executed among many blocks. For example:switch(expression) { case '1': //some statements to execute when 1 break; case '5': //some statements to execute when 5 break; default: //some statements to execute when default; }Visit C switch statement to learn more.
char:-
The char keyword declares a character variable. For example:char alphabet;Here, alphabet is a character type variable.To learn more, visit C data types.
const:-
An identifier can be declared constant by using const keyword.const int a = 5;To learn more, visit C variables and constants.
do...while
int i; do { print("%d ",i); i++; } while (i<10)To learn more, visit C do...while loop
double and float:-
Keywords double and float are used for declaring floating type variables. For example:float number; double longNumber;Here, number is single precision floating type variable whereas, longNumber is a double precision floating type variable.To learn more, visit C data types.
if and else:-
In C programming, if and else are used to make decisions.if (i == 1) printf("i is 1.") else prinf("i is not 1.")If value of i is other than 1, output will be :i is not 1To learn more, visit C if...else statement.
enum:-
Enumeration types are declared in C programming using keyword enum. For example:enum suit { hearts; spades; clubs; diamonds; };Here, a enumerated variable suit is created having tags: hearts, spades, clubs and diamonds.To learn more, visit C enum.
extern:-
The extern keyword declares that a variable or a function has external linkage outside of the file it is declared.To learn more, visit C storage type.
for:-
There are three types of loops in C programming. The for loop is written in C programming using keyword for. For example:for (i=0; i< 9;++i) { printf("%d ",i); }Output0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8To learn more, visit C for loop.
goto:-
The goto keyword is used for unconditional jump to a labeled statement inside a function. For example:for(i=1; i<5; ++i) { if (i==10) goto error; } printf("i is not 10"); error: printf("Error, count cannot be 10.");OutputError, count cannot be 10.To learn more, visit C goto.
int
The int keyword declares integer type variable. For example:int count;Here, count is a integer variable.To learn more, visit C data types.
short, long, signed and unsigned:-
The short, long, signed and unsigned keywodrs are type modifiers that alters the meaning of a base data type to yield a new type.short int smallInteger; long int bigInteger; signed int normalInteger; unsigned int positiveInteger;Range of int type data types
Data types Range short int -32768 to 32767 long int -2147483648 to 214743648 signed int -32768 to 32767 unsigned int 0 to 65535 return:-
The return keyword terminates the function and returns the value.int func() { int b = 5; return b; }This functionfunc()returns 5 to the calling function. To learn more, visit C user-defined functions.
sizeof:-
The sizeof keyword evaluates the size of data (a variable or a constant).#include <stdio.h> int main() { printf("%u bytes.",sizeof(char)); }To learn more, visit C operators.Output1 bytes.
register:-
The register keyword creates register variables which are much faster than normal variables.register int var1;
static:-
The static keyword creates static variable. The value of the static variables persists until the end of the program. For example:static int var;
struct:-
The struct keyword is used for declaring a structure. A structure can hold variables of different types under a single name.struct student{ char name[80]; float marks; int age; }s1, s2;To learn more, visit C structures.
typedef
The typedef keyword is used to explicitly associate a type with an identifier.typedef float kg; kg bear, tiger;
union
A Union is used for grouping different types of variable under a single name.union student { char name[80]; float marks; int age; }To learn more, visit C unions.
void
The void keyword indicates that a function doesn't return any value.void testFunction(int a) { ..... }Here, functiontestFunction( )cannot return a value because the return type is void.
volatile
The volatile keyword is used for creating volatile objects. A volatile object can be modified in an unspecified way by the hardware.const volatile numberHere, number is a volatile object.Since, number is a constant variable, the program cannot changeit. However, hardware can change it since it is a volatile object.Thankyou








No comments
for more information plz do comment and follow my blog.